eccentric lv hypertrophy | severe eccentric left ventricular hypertrophy eccentric lv hypertrophy Progression of the disease can revert to “normal” eccentric LV geometry when post-myocardial infarction remodeling occurs or as a consequence of efficacious . $9,975.00
0 · what is severe concentric left ventricular hypertrophy
1 · treatment for left ventricular hypertrophy
2 · severe eccentric left ventricular hypertrophy
3 · left ventricular hypertrophy life expectancy
4 · eccentric vs concentric hypertrophy heart
5 · eccentric vs concentric cardiac hypertrophy
6 · concentric vs eccentric ventricular hypertrophy
7 · concentric vs eccentric hypertrophy causes
$4,000.00
Patients with eccentric LVH who may initially have HFpEF may develop HFrEF due to progressive loss of contractile function. Therefore, for a . Eccentric left ventricular hypertrophy is induced by an increased filling pressure of the left ventricle, otherwise known as diastolic overload, . Progression of the disease can revert to “normal” eccentric LV geometry when post-myocardial infarction remodeling occurs or as a consequence of efficacious . Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork .
To diagnose left ventricular hypertrophy, a healthcare professional does a physical exam and asks questions about your symptoms and family's health history. The care .
On the other hand, eccentric hypertrophy deals with volume overload due to a significant valvular regurgitation issue or high cardiac index. The systemic pressures will be normal and the peripheral resistance is not .The normal left ventricle size (Table 1) undergoes several types of anatomical cardiac structural adaptations varying from concentric remodeling, eccentric remodeling, concentric hypertrophy, . Left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy consists in an increased LV wall thickness. LV hypertrophy can be classified according to the pattern of wall thickening (symmetrical vs. asymmetrical), the presence of LV dilatation .
Prevalence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes associated with eccentric versus concentric left ventricular hypertrophy in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
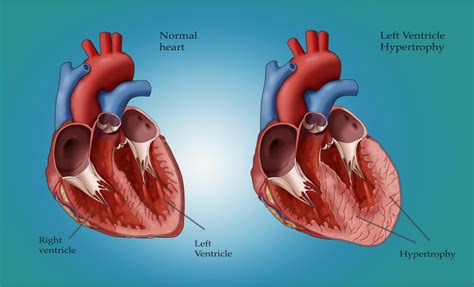
During left ventricular hypertrophy, the thickened heart wall can become stiff. Blood pressure in the heart increases. The changes make it harder for the heart to effectively pump blood.In this blog we describe left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and identify the different categories of concentric, eccentric and concentric remodeling. Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy is an abnormal increase in left ventricular myocardial mass caused by chronically increased workload on the heart, most commonly resulting from pressure overload-induced by arteriolar vasoconstriction as occurs in, chronic hypertension or aortic stenosis. Cross-sectionally, hypertensive patients with more eccentric LV geometry are more likely to have coronary artery disease than patients with concentric LV geometry. 19 Thus, there is a high prevalence of concentric LV geometry during the natural progression of arterial hypertension toward cardiovascular disease, and a high prevalence of .
What is Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH)? Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or . Treatment for left ventricular hypertrophy depends on the cause. It may include medicines, catheter procedures or surgery. It's important to manage conditions such as high blood pressure and sleep apnea, which can cause blood pressure to be higher. Left ventricular hypertrophy is a form of cardiac remodeling that causes the heart wall muscle to thicken, which leads to an increase in LV mass (LVM). There are different sub-categories that fall into the diagnosis of LVH, which includes concentric, eccentric and .Chronically or intermittently elevated blood pressure (BP) increases systemic pressure and volume overload, with increased workload on the left ventricle and ultimately left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy (LVH).
LV hypertrophy is often a precursor to subsequent development of heart failure. Cardiovascular imaging plays a key role in the assessment of LV hypertrophy. Echocardiography, the first-line imaging technique, allows a comprehensive assessment of .
what is severe concentric left ventricular hypertrophy
treatment for left ventricular hypertrophy
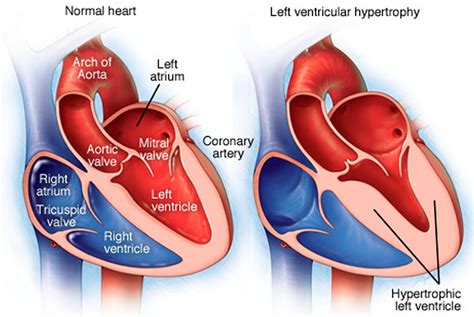
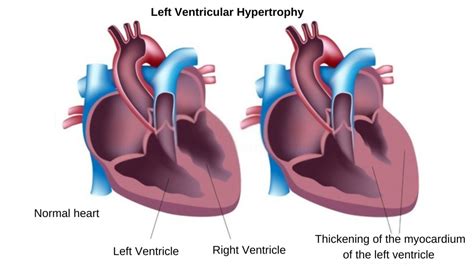
Prevalence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes associated with eccentric versus concentric left ventricular hypertrophy in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
During left ventricular hypertrophy, the thickened heart wall can become stiff. Blood pressure in the heart increases. The changes make it harder for the heart to effectively pump blood.
In this blog we describe left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and identify the different categories of concentric, eccentric and concentric remodeling.
Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy is an abnormal increase in left ventricular myocardial mass caused by chronically increased workload on the heart, most commonly resulting from pressure overload-induced by arteriolar vasoconstriction as occurs in, chronic hypertension or aortic stenosis.
Cross-sectionally, hypertensive patients with more eccentric LV geometry are more likely to have coronary artery disease than patients with concentric LV geometry. 19 Thus, there is a high prevalence of concentric LV geometry during the natural progression of arterial hypertension toward cardiovascular disease, and a high prevalence of . What is Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH)? Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or . Treatment for left ventricular hypertrophy depends on the cause. It may include medicines, catheter procedures or surgery. It's important to manage conditions such as high blood pressure and sleep apnea, which can cause blood pressure to be higher. Left ventricular hypertrophy is a form of cardiac remodeling that causes the heart wall muscle to thicken, which leads to an increase in LV mass (LVM). There are different sub-categories that fall into the diagnosis of LVH, which includes concentric, eccentric and .
Chronically or intermittently elevated blood pressure (BP) increases systemic pressure and volume overload, with increased workload on the left ventricle and ultimately left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy (LVH).
severe eccentric left ventricular hypertrophy
left ventricular hypertrophy life expectancy
$6,118.00
eccentric lv hypertrophy|severe eccentric left ventricular hypertrophy